By Clarence Page
Chicago Tribune
WWR Article Summary (tl;dr) Every year, The Committee to Protect Journalists releases “Attacks on the Press,” a book-length analysis of which countries are abusing journalists the most. This year is different. In response to growing concerns, the new “Attacks” is focused on sexualized violence, online harassment and other intersections of gender and press freedom. In addition, women leaders in the field of journalism are sharing their experiences to bring these attacks out the of the shadows.
Chicago Tribune
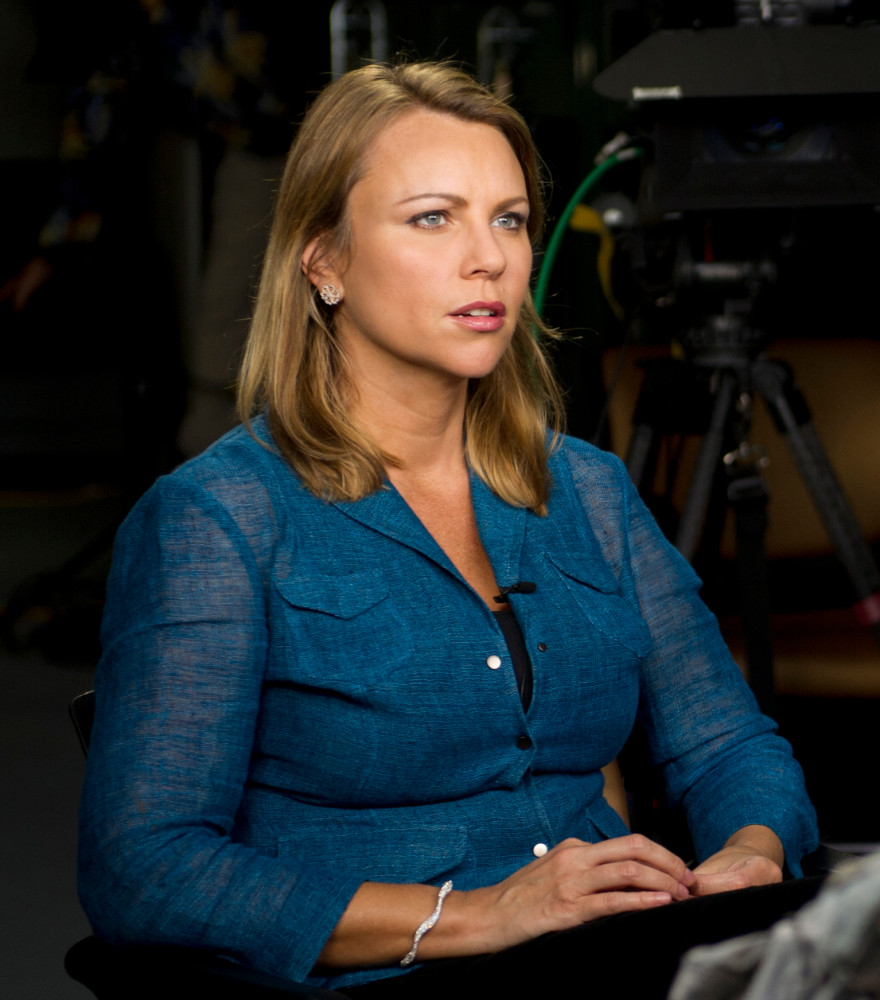
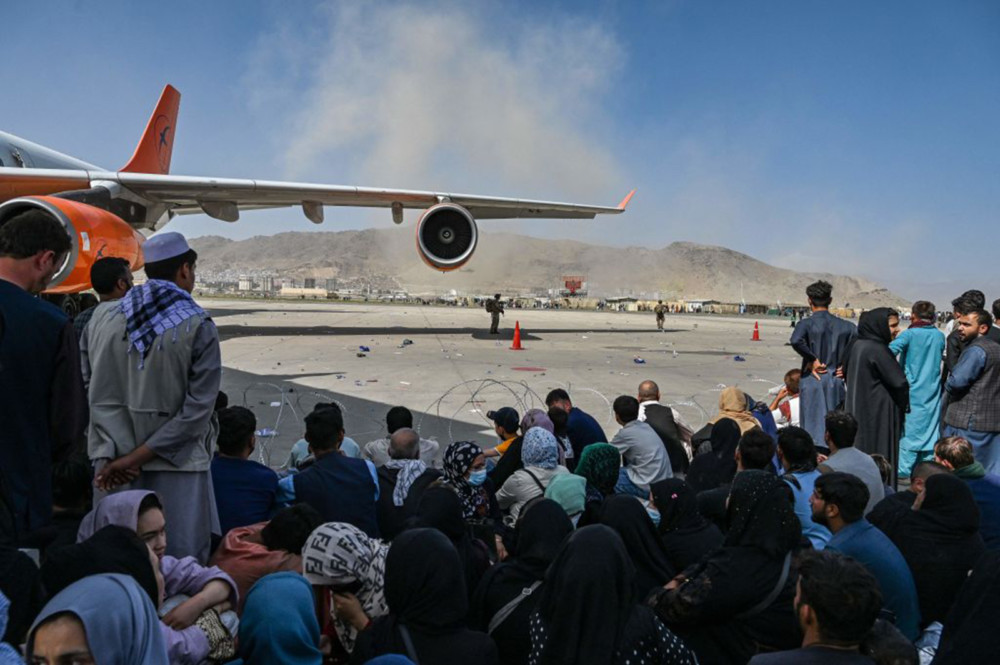
Five years have passed since CBS “60 Minutes” correspondent Lara Logan was sexually assaulted by a mob of crazed men, and rescued by a small group of brave Egyptian women, in Cairo’s Tahrir Square during the fall of Hosni Mubarak’s dictatorship.
The widespread coverage given to that attack brought a new focus to a growing problem that had been looming in the shadows for years: sexual assault against journalists.
In the first four months after Logan’s attack, the New York-based Committee to Protect Journalists interviewed more than four dozen journalists who had undergone sexual violence. The offenses ranged in severity from gang-rape to aggressive groping by multiple attackers.
Unfortunately, the usual conflict between safety and press freedom on such assignments is complicated by the double-bind in which many female journalists find themselves: They want the dangers of sexual violence to be acknowledged, but they don’t want that knowledge to give their editors cold feet about sending women on dangerous assignments.
New York Times reporter Kim Barker, for example, whose war memoir, “The Taliban Shuffle,” has been turned into a Tina Fey movie, recalled in a 2011 ProPublica essay how she was grabbed and groped as a Chicago Tribune reporter in Pakistan in 2007.
“I knew other female correspondents who weren’t so lucky, those who were molested in their hotel rooms, or partly stripped by mobs,” she wrote. “But I can’t ever remember sitting down with my female peers and talking about what had happened, except to make dark jokes, because such stories would make us seem different from the male correspondents, more vulnerable.”
She would never tell my bosses, she said, “for fear that they might keep me at home the next time something major happened.”
Indeed, even the Committee to Protect Journalists, on whose board I am honored to sit with Logan and other distinguished colleagues, had unwittingly joined in the silencing of those women. CPJ kept tabs on how many journalists were killed or imprisoned around the world, Barker noted, but did not keep data on sexual assault and rape, partly because “most journalists just don’t report it.”
That’s changed. Every year CPJ releases “Attacks on the Press,” a book-length analysis of which countries are abusing journalists the most. This year is different. In response to growing concerns, the new “Attacks” is focused on sexualized violence, online harassment and other intersections of gender and press freedom.
In an all-women panel sponsored by CPJ and moderated by Martha Raddatz, ABC News chief global affairs correspondent, at Washington’s Newseum last week (viewable at CPJ’s website, www.cpj.org), Logan recalled how she had been pressured by male colleagues to join other journalists who were leaving war-torn Iraq.
“I remember being heavily criticized, because they said, ‘You just want to get your face on TV. … But if something happens, we’re going to have to come get you’,” she recalled. “If I was a young guy, and I wanted to stay, no one would have said anything like that.”
Besides, as the panel pointed out, women are not the only victims of sexual violence. Male journalists also have been targeted, usually in captivity or detention, even if they tend to be even more reluctant than the women to report the crime or talk about it.
One notable exception, Umar Cheema, a prominent Pakistani political reporter, described to CPJ being abducted, tortured and sodomized with a wooden pole in an Islamabad suburb in 2010 in retaliation for his political reporting.
His decision to speak out “has made me stronger and made my enemies more cowardly,” he told CPJ in 2011. “Their efforts to intimidate me backfired.”
As Logan said in her 2011 “60 Minutes” interview about the attack, women journalists “do it for the same reasons as me, they are committed to what they do. They are not adrenaline junkies, you know, they’re not glory hounds, they do it because they believe in being journalists.”
What is to be done? I think we make a mistake, whether as news content providers or news consumers, if we make the false choice between safety and good journalism. We need to have both. Women have shown in growing numbers that they deserve a chance to prove themselves as much as men do.
We also need to acknowledge that discrimination and harassment are problems that women tend to face more often and intensely than men do. We need to talk more about it, not try to hide it.
___
ABOUT THE WRITER
Clarence Page is a member of the Chicago Tribune Editorial Board.