By Stacey Burling
The Philadelphia Inquirer
WWR Article Summary (tl;dr) First we were told not to wear the masks, then we were told to make them and now, in some places, they are mandatory. Stacey Burling sorts out some of the confusion.
Philadelphia
In a widely circulated video clip from a hearing last week on mandatory mask wearing in Orange County, Calif., an angry woman told officials she feared that masks made her re-breathe her own carbon dioxide, a waste product when we exhale.
“You’re telling me that I have to breathe in CO2 when God gave this body the ability to extract that from my body, and now you want me to put it back in my body,” she said.
After the hearing, the county changed the requirement to a recommendation. Then the state on Thursday required masks in most settings outside the home.
Donna Lea Merritt, a Berks County, Pa., woman who attended several protests against Pennsylvania’s coronavirus lockdown earlier this spring, also worries about CO2 and masks. She wears a mask only when she has to and even then “forces the issue.”
“It decreases your oxygen intake,” said Merritt, an alternative delegate at this summer’s Republican National Convention. “I think it increases your toxin inhalation.” That, she said, puts her immune system under stress and increases the odds of infection. She said she gets her information online, including from a medical Facebook show called The HighWire With Del Bigtree.
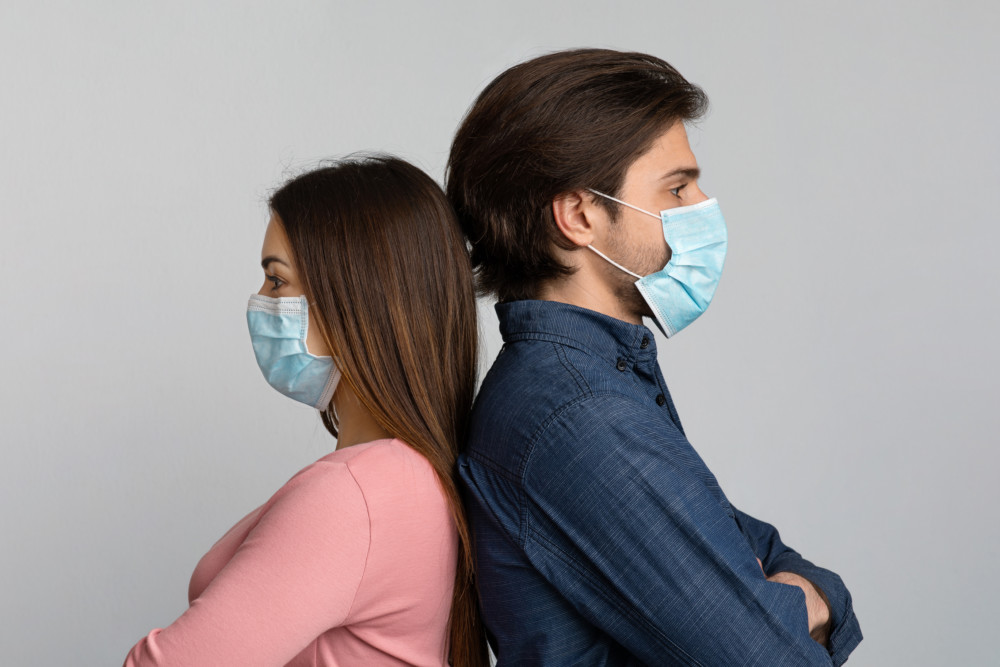
Initially seen as a nonpartisan way to fight the coronavirus, masks are now part of this country’s culture wars, a focal point in battles over the balance among safety, personal freedom and economic well-being.
The president resists wearing them and so do some Republican lawmakers.
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi on Wednesday required that masks be worn during committee meetings after some Republicans refused to do so.
Some who oppose masks downplay the dangers of the new virus, which causes mild illness in most but has also killed over 120,000 Americans.
Others, though, raise medical concerns. Henry Fraimow, an infectious disease doctor at Cooper University Hospital, said he heard of health-care workers who were worried in March and April about breathing problems from mask use. “It’s picked up a life of its own,” he said.
Shiva Ayyadurai, a biological engineer who is running for Senate as an anti-“deep state” Republican in Massachusetts, says the cloth and surgical masks most of us wear are too porous to stop the virus. He says we’d be better off strengthening our immune systems with good diets, time outside (for vitamin D), and, if necessary, vitamins. In a video, Ayyadurai, who is one of Merritt’s information sources, also said that masks are antisocial and hamper relationships that strengthen immunity.
Russell Blaylock, a retired Mississippi neurosurgeon who now does nutrition research and edits the Blaylock Wellness Report, has written that masks can affect intake of both oxygen and carbon dioxide as well as immune functioning.
Infectious disease experts said masks are an imperfect defense against the coronavirus but evidence has mounted that, when combined with social distancing, eye protection, and frequent hand washing, they can slow its spread. Their primary benefit is not to an individual wearer, but to others. When a mask wearer coughs, sneezes, or simply breathes, the mask acts as a barrier that blocks the flight of virus-laden droplets. “A lot of the droplets never make it out, and then the ones that do don’t go very far,” Fraimow said.
This is especially important in a disease where people without symptoms can spread the virus. Without symptoms, there’s no way to know when to stay away from others, so, the thinking goes, we should all assume we might be sick and wear a mask.
As Pennsylvania’s health department is fond of saying, “My mask protects you, your mask protects me.” Infectious disease experts said this has been a hard concept for many to understand.
It has not helped, experts said, that public health messaging on masks has changed radically since the early days of the pandemic and has remained inconsistent. When the virus first arrived in the United States, protective equipment like masks was in such short supply that health-care workers couldn’t get enough of it. Experts then argued that the masks wouldn’t offer much protection to the rest of us.
Ravina Kullar, a spokesperson for the Infectious Diseases Society of America and an infectious disease consultant to Los Angeles nursing homes, was among those who initially recommended against masks. She’s changed her mind. “The way this virus is behaving is nothing like other viruses we’ve seen,” she said.
As for oxygen and CO2, infectious disease specialists said there’s no evidence to support the idea that cloth and surgical masks, the blue rectangular masks typically worn by nurses and doctors, lead to breathing problems. They don’t fit tightly enough to impede air flow or trap carbon dioxide.
“We don’t have ERs full of people who wore a mask and became sick because they were wearing a mask,” said William Schaffner, an infectious diseases specialist at Vanderbilt University Medical Center.
They can be uncomfortable, though, and they make some people feel a little claustrophobic.
“It’s cumbersome to have a mask on, and that’s what people notice,” said Amesh Adalja, an infectious disease doctor at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security.
Kullar said Americans aren’t used to wearing masks. “I think that people are trying to find reasons not to wear masks and questioning everything,” she said.
N95 masks are more complicated. They are better at filtering tiny viruses than the other masks and fit tightly against the face. There has been a shortage of N95s, and they have been reserved for medical workers who use them around coronavirus patients who are coughing or getting procedures that can force virus into the air.
There is some evidence that N95s can lead to changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels when used for long periods, especially by people who are obese or have chronic lung issues. Adalja said they are not meant for long-term use, and doctors try to take breaks from them. They have not been recommended for the general public. However, any breathing issues related to the masks do not lead to serious health problems, he said.
Fraimow said medical workers have been wearing N95s for longer periods than in the past without experiencing health problems. Some even cover them with surgical masks. This can make it feel harder to breathe or do things like climb stairs. They can also be uncomfortable.
Schaffner said CO2 is not the big issue with masks. “The big issue with masks,” he said, “is that people aren’t wearing them.”
___
Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.