By David Tarrant
The Dallas Morning News
WWR Article Summary (tl;dr) Genetic medicine has long held the promise of extraordinary advances in healing and treatment. But new, faster, cheaper techniques, including next-generation sequencing, are seeing that promise realized in ways that are saving lives.
The Dallas Morning News
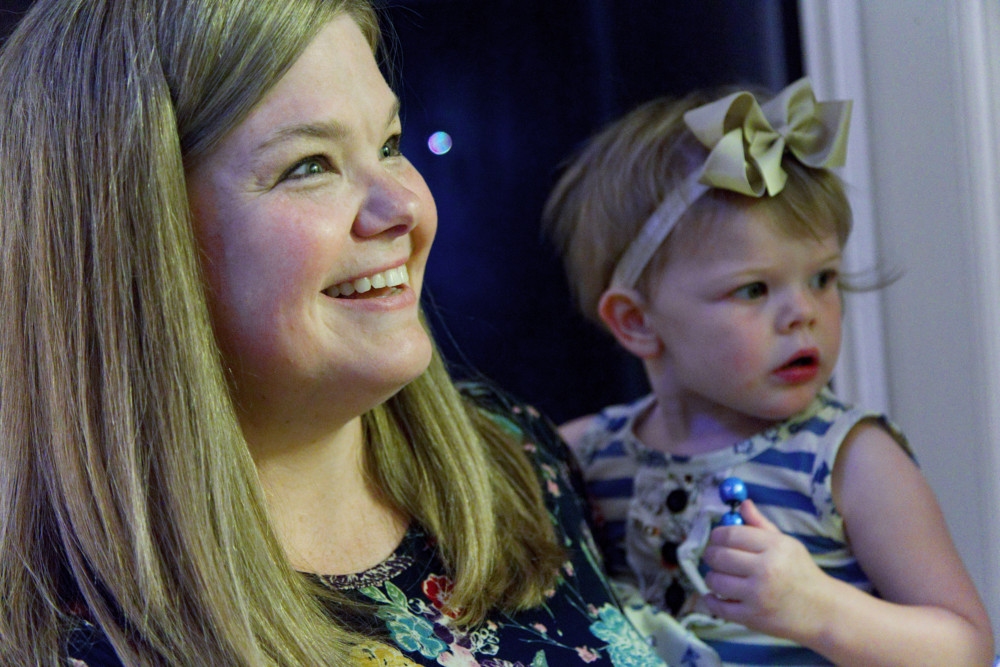
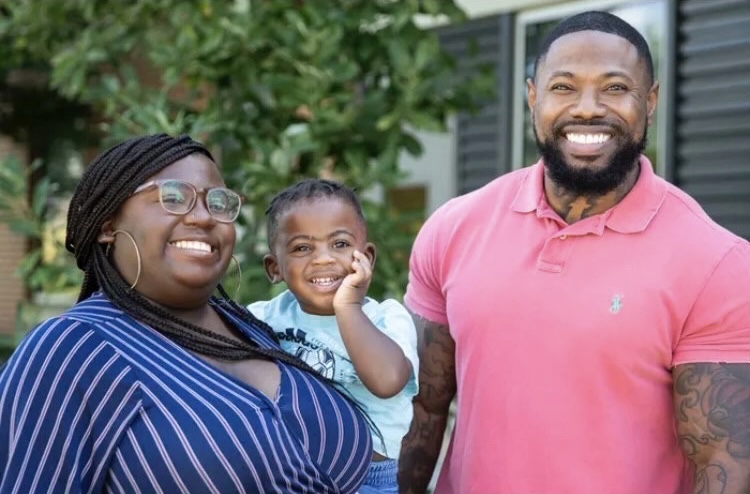
Four days after Jessica Hitt gave birth to her first child, Olivia, the new mother became delirious.
She started walking into walls and talking gibberish. Her husband rushed her to Medical City Arlington, the same hospital where she had given birth. Her health rapidly deteriorated. Twice she received the last rites from a priest.
Doctors and nurses worked furiously to figure out what was wrong. Tests showed dangerously high levels of toxic ammonia in her blood. But why? Nothing in Hitt’s medical history suggested this uncommon disorder.
The doctors treating Hitt were baffled, so they reached out to Dr. Markey McNutt, a clinical geneticist at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Hitt’s case was exactly the sort of strange medical puzzle McNutt specializes in.
Genetic medicine has long held the promise of extraordinary advances in healing and treatment. But new, faster, cheaper techniques, including next-generation sequencing, are seeing that promise realized in ways that are saving lives.
“Only in the last 10 years has this really become prominent, and only within the last two years has the cost come down so that it’s cost-effective,” said McNutt.
For Hitt, it very well might have meant the difference between life and death.
‘SOMETHING’S NOT RIGHT’
Hitt gave birth to Olivia at 10:22 p.m. on May 4, 2016. Everything had gone well and the new mom and her husband, Marshall, enjoyed those first hours and days as new parents. But back home, Jessica suddenly was not herself, her husband recalled.
“I came into the kitchen and asked her something that should have not been confusing at all, but she wasn’t getting it,” Marshall Hitt said. “And I asked her over and over again. And she’d say ‘I don’t understand what you’re saying.’ Finally, I realized something’s not right.”
His wife was acting like a drunken sailor on leave. She was staggering, walking into walls, acting aggressively, cursing.
“She would yell and get very angry at me. She would try and find the keys to leave and end up walking into the room like a zombie,” Marshall Hitt said.
Jessica Hitt can only remember feeling confused and disoriented.
“I did not understand what was going on at the time,” she said. “I was out of it. I would ask questions and not understand what they were telling me.”
CRITICALLY ILL
Doctors at Medical City Arlington determined that Hitt’s ammonia levels were running too high. They put her on dialysis to clean her blood. They ran multiple tests, including a CAT scan and MRI.
“They kept trying to figure out why I had high ammonia levels,” Hitt said. “Then they started consulting with Dr. McNutt.”
In adults, an excessive level of ammonia is typically the result of viral hepatitis, alcoholic cirrhosis, or medications and drugs that can damage the liver. None of those conditions applied to Hitt.
“So when there were none of the common explanations we typically see in adults, they called us to see if this is one of the genetic conditions we typically see show up in childhood,” McNutt said.
At first, McNutt helped manage Hitt’s treatment by phone. But after her condition deteriorated, she was transferred to UT Southwestern, where the new mom arrived in critical condition. Not only were her ammonia levels high, her red blood cells had started breaking apart, causing her blood levels to plummet.
GENETIC DISORDER
McNutt suspected that Hitt was suffering from a defect in the urea cycle, which is how the body gets rid of excess nitrogen created by the breakdown of protein. Ammonia is a normal byproduct of processing nitrogen in the body. The urea cycle is the way of converting the toxic ammonia into urea, which is flushed out in the urine.
When the cycle doesn’t work as it should, ammonia builds up. And if the ammonia reaches the brain through the blood, it can cause the brain to swell, resulting in coma, permanent brain damage and even death.
A urea cycle disorder can be the result of a genetic defect. “Typically, we diagnose them in childhood,” said McNutt, also assistant professor of pediatrics and internal medicine at UT Southwestern. “The high ammonia levels cause infants to be really sleepy.”
Hitt’s condition began to stabilize after days of intensive treatment, including dialysis and blood transfusions. She was released after a week at UT Southwestern and put on medication to help keep her ammonia levels steady. She continued getting monthly checkups.
In the meantime, though, McNutt wanted to pinpoint the exact genetic defect that had caused her urea cycle disorder. Hitt agreed to take part in a genetic research study that lasted about a year. At the end of the study, McNutt was finally able to explain exactly what happened to his patient.
The problem turned out to be a flaw in Hitt’s genetic coding known as N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency. In simpler terms, it means the enzyme that is supposed to trigger the first step in Hitt’s urea cycle did not work.
But it didn’t cause problems until Hitt had a major health event, the birth of her baby.
PAPER SHREDDER
McNutt compared her situation to using a paper shredder meant to handle 10 sheets of paper. But if the shredder has a defect, it can shred only one or two pieces of paper. When someone tries to shove a hundred pieces of paper into the shredder, it stops working.
“It’s going to mess things up,” McNutt said.
When Hitt experienced birth and post-pregnancy changes to her body, it overwhelmed her defective urea cycle. After giving birth, the body has a lot of work to do in processing and disposing of the extra blood that builds up during the pregnancy. The body also reduces the size of the uterus by about half. That floods the blood with excess protein that has to be processed as waste. Hitt’s body couldn’t handle that.
Ten years ago, Hitt’s condition could have been fatal. But thanks to doctors and researchers like McNutt, cases like Hitt’s are becoming less mysterious each year.
“We are learning how often they occur. We don’t actually know,” McNutt said.
“We think they’re rare. When we test for them more frequently, we’ll get a better idea,” he said.
Through more newborn screening and more awareness of genetic disease, doctors have been able to identify moderate and even milder forms of these conditions, which they can treat immediately.
McNutt says Hitt was lucky that not only could they diagnose her problem as a rare genetic disease, they also had the treatment for it, a set of pills that she takes twice a day.
“It kicks off my urea cycle to process the excess nitrogen or ammonia created by the breakdown of protein,” Hitt said.
MOVING ON WITH LIFE
Hitt is pregnant again. Her doctors told her it was OK. “They’re just going to monitor me closely,” she said.
This time she not only has her genetic specialist but also a team of high-risk pregnancy specialists at UT Southwestern. “I’m feeling really good,” Hitt said.
“I’m very grateful that Dr. McNutt was able to help us figure out what was going on, and get answers and move on with life,” Hitt said.
She’s 22 weeks pregnant, a little more than halfway there.
And Olivia, who is now 2, can look forward to having a little brother in her life.