By Geoffrey Mohan
Los Angeles Times
WWR Article Summary (tl;dr) It hasn’t always been easy for Pam Marrone, founder and CEO of “Bio Innovations.” The company is one of the leading startups focused on ecologically based pest management. In this article, she shares her journey.
Los Angeles Times
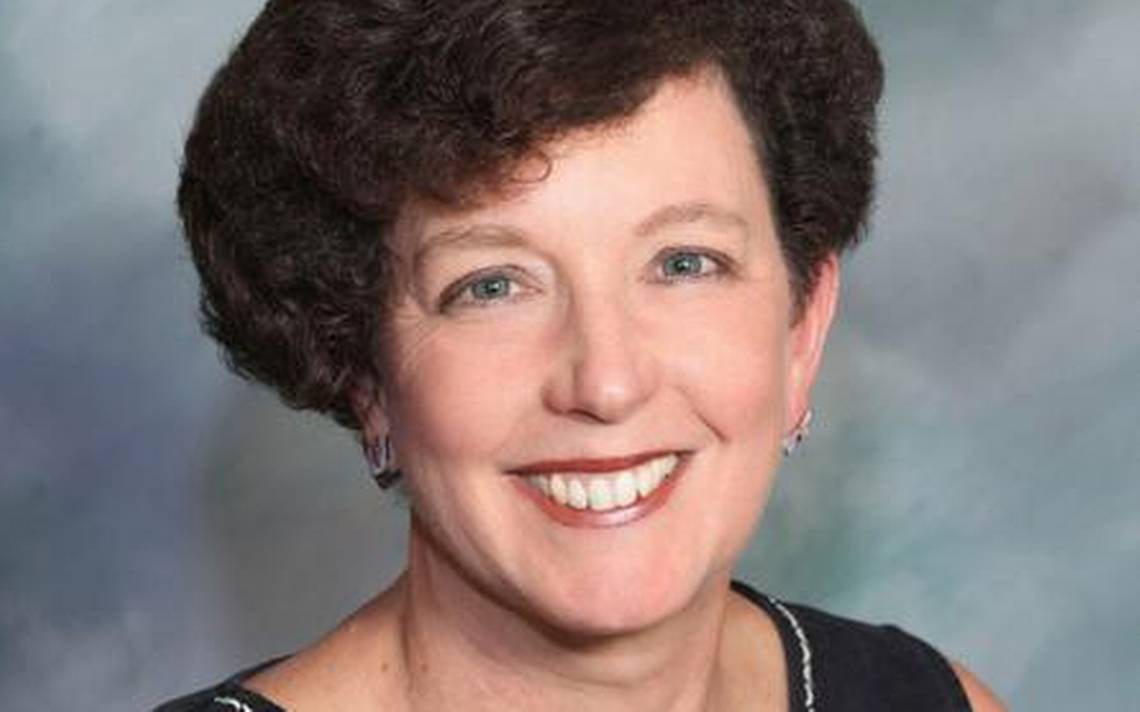
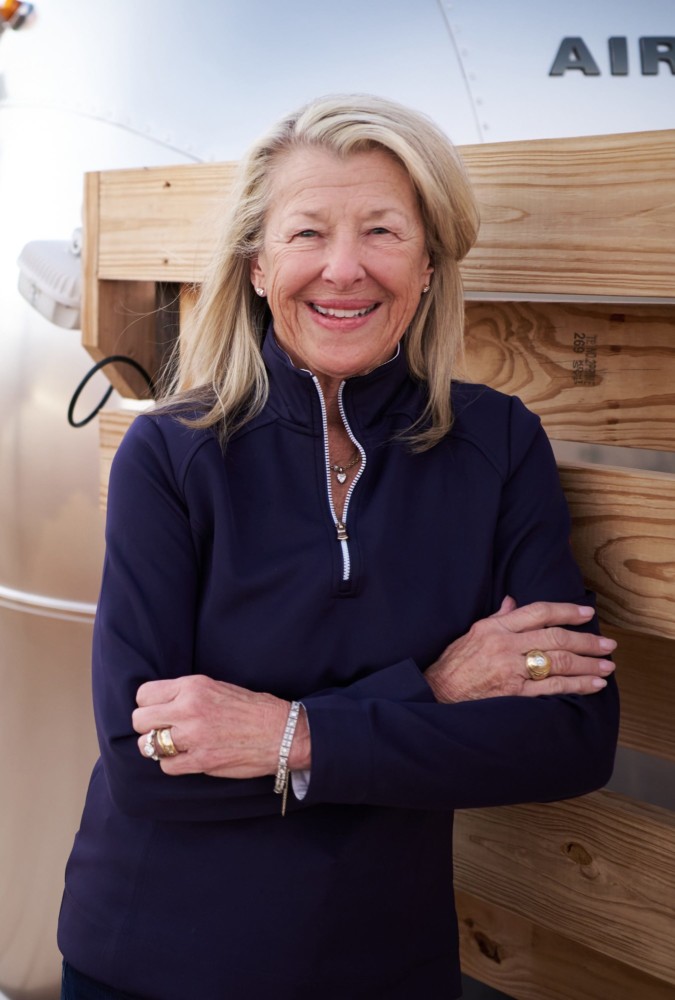
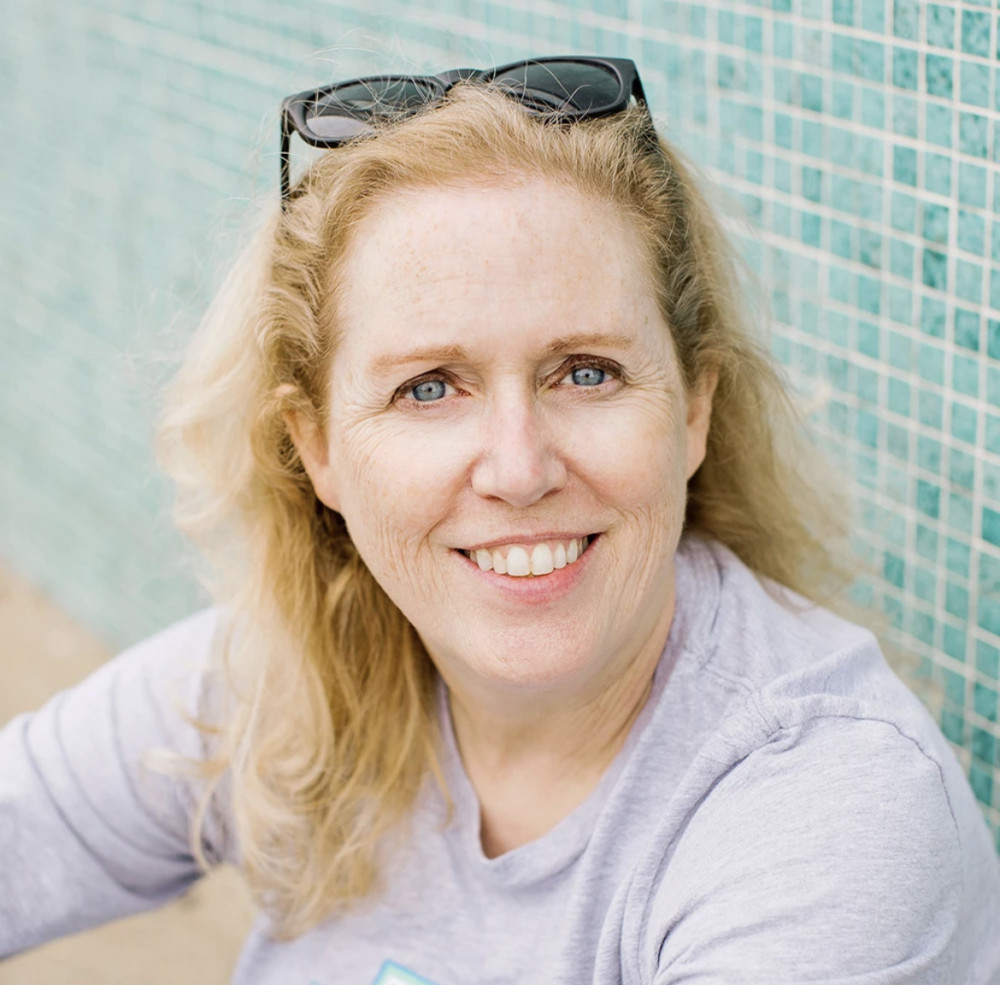
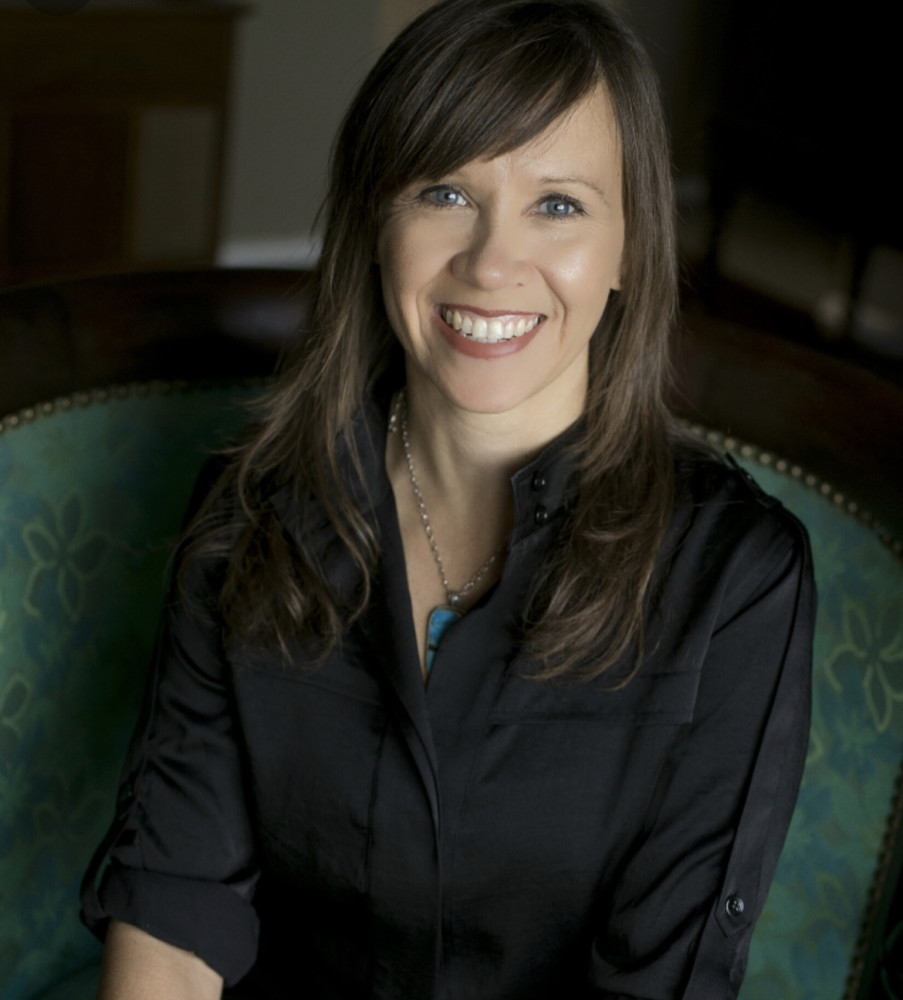
The gig: Pam Marrone, 60, heads Marrone Bio Innovations in Davis, Calif., a leader among startups competing for a slice of the market in natural pesticides.
Unlikely start: Feeding worms was Pam Marrone’s first job at U.S. agrochemical giant Monsanto. That may seem like an inglorious assignment for a budding entomologist with a freshly minted doctorate from North Carolina State University. But in 1983, no one had yet figured out a way to keep the southern corn root worm alive in the laboratory long enough to study why it succumbed to a lowly soil bacterium that farmers had used since the 1950s to protect their crop.
“Oh, my God, what have I accepted?” Marrone recalled thinking. “I took every ingredient possible that was in a failed, not-quite-good-enough artificial diet, changed it by plus or minus 10 percent and came up with a diet that was good enough.” That diet became the industry standard for rearing Diabrotica undecimpuncta.
“I have to laugh now,” Marrone said. “That was my claim to fame.”
More importantly for Monsanto, the artificial diet ultimately allowed scientists to splice a strand of genetic code from bacteria into corn, effectively giving the crop a built-in pesticide.
Bumpy road: Marrone’s path from genetically modified organisms back to her original avocation, finding natural ways to fight agricultural pests, was about as nasty as feeding worms.
Her first startup, Agraquest, was scheduled to go public Sept. 12, 2001, her attorneys had to flee the south tower of the World Trade Center.
New investors and a new funding round vastly diluted the value of her founder’s stake, so she never reaped the windfall of the company’s eventual sale to Bayer for $425 million.
Marrone tried again, founding her company in 2006 and taking it public in a $57-million offering in 2013.
For a while, Marrone Bio Innovations was an up-and-comer in a burgeoning tech hub sprouting around the University of California, Davis. But a year later, Hector Absi Jr., her chief operating officer, abruptly resigned. An internal investigation showed Absi had concealed a scheme to inflate the company’s revenue by million, netting him more than 0,000 in bonuses, stock sales and illegitimate expenses, according to the Securities and Exchange Commission, which charged him with fraud in February.
buy viagra capsules generic buy viagra capsules online no prescription
Those charges are pending.
Marrone paid a fine of $1.7 million to the SEC, and settled ensuing shareholder lawsuits for a reported $12 million, moves that contributed to layoffs and a painful restructuring.
The company’s stock, once valued at $19, now trades at $1.70.
Turnaround: Despite the company’s negative cash flow, several analysts think Marrone Bio Innovations is going in the right direction, largely based on its product pipeline, three consecutive quarters of revenue growth, and some strategic partnerships with companies such as Koch Agronomic Services.
“All that’s behind us,” Marrone said. “We restructured the company to be smaller but more focused. We’re improving our gross margins. We’re focused on growth – growing our products, the five commercialized products that we have, and then bringing the next set of products to the market.”
Believing in the mission: The company is focusing on a new microbe that can kill pests that have developed resistance to glyphosate pesticides and another microbe that can replace chlorine treatments as a way to control invasive mussels clogging industrial pipes and threatening native species in lakes and rivers.
“I’m in it because I believe these products should be the base of ecologically based pest management. That’s how I was trained. And that’s where the future is. We’re at the tipping point with biologicals. Now, they’re becoming mainstream. I’m in it more for changing agriculture. I got through it because we believe in what we are doing. We have great products, and we have more coming, and this is the future. So we really focus on the employees who are here.”
Key management lesson: “As founder and CEO, you can underestimate how much time you have to spend in making sure your culture stays where you want it. Because when you have new people who come in, with other ideas, they can drift the culture into different ways that veer from the vision and strategy of the company.”