By Colleen Mastony
Chicago Tribune.
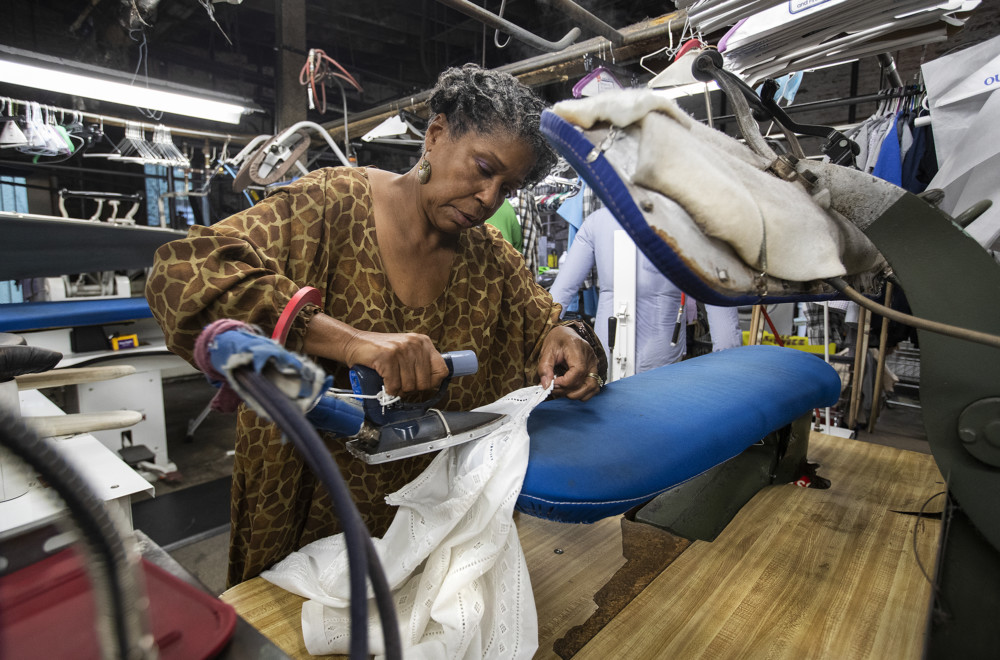
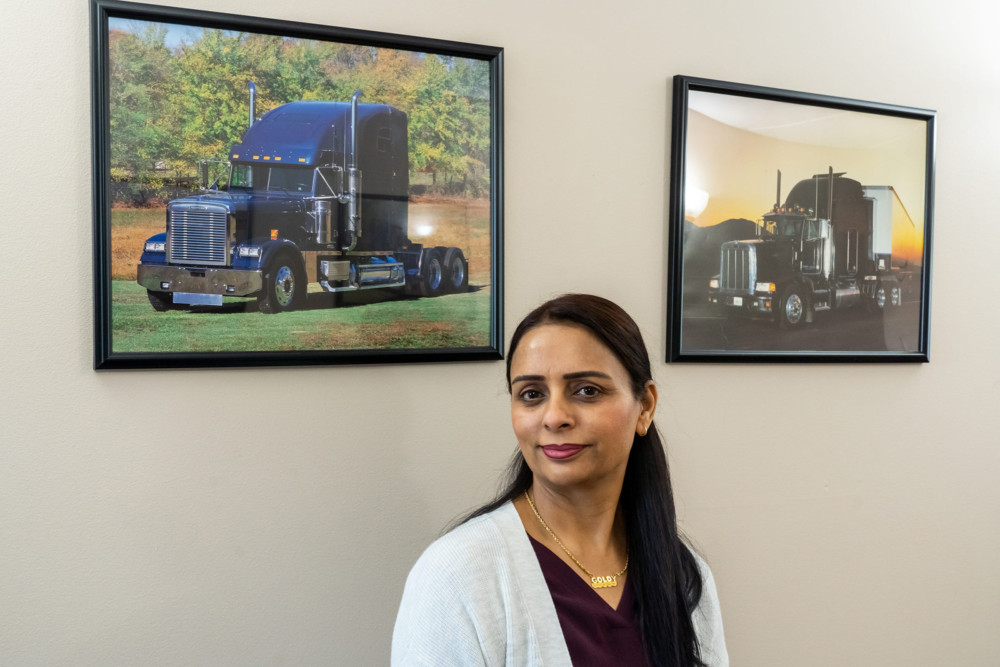
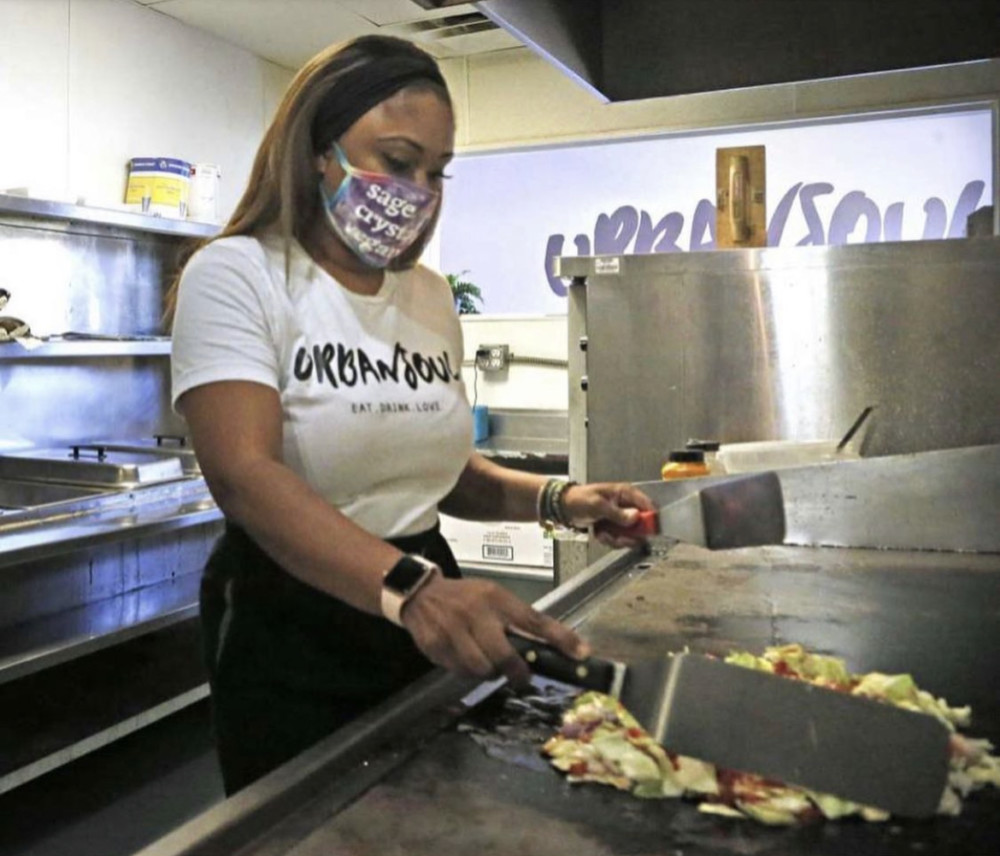
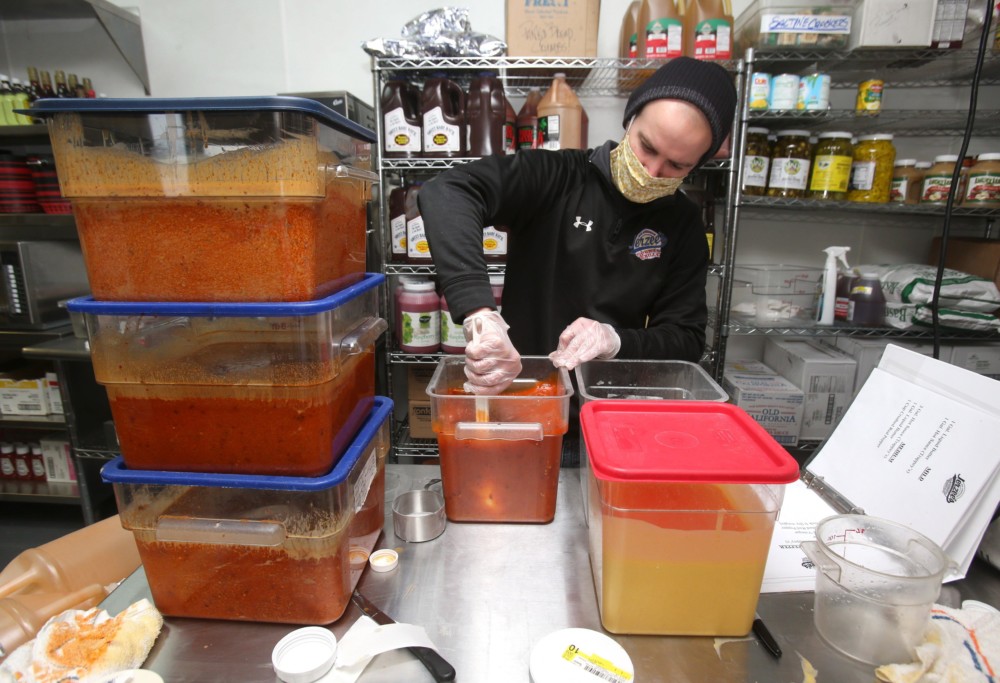
Drew McDonough walks quickly past the 50-pound bags of brown sugar and the huge tubs of chocolate frosting. He takes a second to clock in at a computer, dresses in his bakery clothes (hairnet, work shirt, apron), and then speed-walks toward the stainless steel table where, five days a week, he packages cups of sticky toffee pudding.
When his boss inquires about his weekend, McDonough responds with brisk one-word answers and barely makes eye contact. But that is fine with Jean Kroll, owner of the Sugar & Spice Extraordinary Sweet Treats commercial bakery in Evanston, who simply points her new hire toward the racks of golden brown cakes.
“We have 800,” she says. “Can you start by dating the sleeves and then getting some boxes?”
For the rest of the four-hour shift on this cold December afternoon, the quiet, dark-haired 27-year-old moves so quickly he seems set on fast-forward. He boxes cakes, stacks them on a hand cart, labels them for shipment and, when he’s done, carefully sweeps the floor.
McDonough has autism. The fact that he also has a job at the bakery is something that he says is “probably a miracle.”
“I’m working 20 hours a week, which my parents are very happy about,” he said. “It feels as happy as can be.”
This past summer, McDonough and two other men with autism arrived at the bakery as part of a six-week unpaid internship. But there was one important twist: As the men learned to measure sugar and package cakes, a graduate student from Northwestern University’s Kellogg School of Management carefully tracked their productivity. The question: Did it make good business sense to hire someone with a disability?
For Kroll, a 50-year-old entrepreneur who had plowed her life savings into the bakery, that was a critical question.
“Small businesses hire based on economics,” Kroll said. “Most of us are not big enough to hire based on a philanthropic approach.”
The story of how — at the end of the internship — she offered paid positions to McDonough and two other men with autism is one of luck and goodwill. But it is also, according to Kroll, a story of a clear-eyed business decision.
“People always say, ‘That’s such a nice thing to do,'” said Kroll, referring to her decision to hire the men. “I say, ‘Yes it is nice. But it’s also a smart thing to do.'”
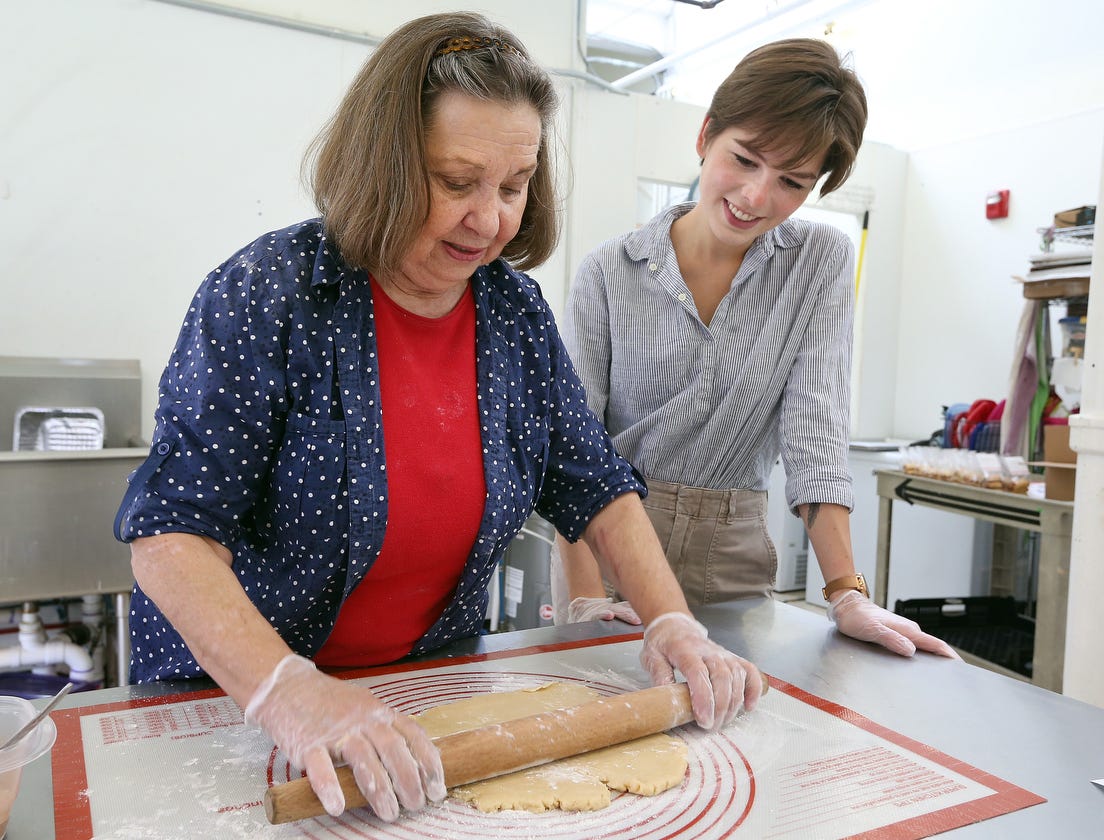
Two years ago, Kroll moved her commercial bakery into a 10,000-square-foot facility tucked in an industrial strip off Dempster Avenue. A few doors down was a nonprofit called Have Dreams, which provides services to people with autism.
Shortly after the move, Kroll’s landlord mentioned that her new neighbors — the men and women with autism — were always looking for job training.
“Maybe they could help you build boxes,” the landlord suggested.
Soon after, Kroll invited a group of five men with autism to help her construct and label boxes for her chocolate chip, oatmeal raisin and signature shortbread cookies. She had no experience with people with disabilities. But when a young man put together a box and, with a huge grin, declared: “Look what I did!” Kroll was charmed.
For a year and a half, the men came every week.
There was a tall, blond-haired man named Zach, who loved to talk and ask questions, and Michael, who was playful and cracked jokes, and Jimmy, who was so focused that he could label boxes as fast as any worker.
“They came every week and were smiling and enthusiastic,” Kroll recalled. “My staff really warmed to them too.”
One day, an administrator at Have Dreams asked if Kroll might have other jobs for the men.
Kroll’s answer was firm and immediate.
“No,” she said.
After she went home that night, she couldn’t stop thinking about what she had said.
“I was so angry with myself,” she recalled. “They were such a great group of young people.”
Around that time, Kroll had begun negotiations with a client whose line of baked goods would require labor-intensive packaging.
The work could have been automated, but Kroll didn’t have the $80,000 she estimated it would cost to buy the equipment.
She thought of the men from Have Dreams and picked up the phone.
“I think I might have a job for the guys,” she said.
Over the following weeks, Kroll and a team from Have Dreams came up with a plan to establish a job training program at the bakery and eventually landed a $125,000 grant from the Chicago-based Coleman Foundation. The money came with a unique prerequisite: It required Have Dreams to hire a Master of Business Administration student to collect data on the men’s productivity.
“What we saw was the opportunity to build a business case,” said Clark McCain, senior program officer at the Coleman Foundation.
“That’s a language that other business owners will be able to understand.” If the bakery program succeeded, the data could be used to persuade other business to hire people with disabilities.
The six-week training program targeted high-functioning people with autism who had completed high school or college but who had trouble keeping a job. The goal was to teach not only job skills but also softer skills such as initiative, independence and communication that are often the key to employment.
On June 24, three men arrived at the bakery, where the air is heavy with the scent of baking chocolate, and where racks of ginger cakes spin in industrial-sized convection ovens.
One man was so nervous his hands shook. A second arrived late. The third, when the work began, moved as slow as molasses.
“I remember thinking, ‘Oh my God, now what?'” Kroll recalled.
In those first weeks, the men’s presence was undeniably disruptive. With two job coaches, the Northwestern student and Kroll in tow, they created what Kroll recalled as a “small circle of chaos” that moved around the bakery. The 10 other employees were, at first, confused about the men’s role. They wanted to know: Why were the men there? And what, exactly, was autism?
Kroll reassured her staff as best she could and set about training her new interns.
The first week, the men worked alone, learning how to measure sugar and package cakes. By the third week, they attempted to work as a team — a challenge for many with autism.
Slowly, the men grew more comfortable. The job coaches stepped away and allowed each man to take a turn as team leader.
“We set the bar low for some of the productivity tests, and we were getting low results,” Kroll recalled. “So I said, ‘I am going to raise the bar really high.’ And they met that goal. So I raised the bar again, and they met it again.”
One afternoon, Kroll turned to her production manager and said: “Did you notice the guys processed 500 cakes today?” The manager — who had been slow to buy in to the effort — gave a small smile and a nod of approval.
By the end of the six weeks, the metrics that tracked the men’s productivity for portioning sugar, labeling boxes and dating the cakes showed that they could work about 80 percent as quickly as a typical bakery worker. For Kroll, that was a break-even point that meant it would make sense to hire them for an entry-level, minimum-wage position and allow more experienced, higher-paid workers to focus on more complex tasks.
When an official from the Coleman Foundation came for a visit in August, Drew McDonough — whose hands used to shake — proudly gave a tour of the bakery. Then McDonough joined the other men on a small assembly line.
“They worked together without a coach and did a wonderful job,” recalled Kroll. “Everyone looked at each other, and we were all thinking, ‘This works. This makes sense.'”
The bakery was about to enter the busy holiday baking season. “I started thinking, ‘I’m going to be really busy going into the fall. I’m going to need these guys,'” Kroll said.
A few days later, she offered each of the men a Christmas-season position that would pay them $8.25 an hour.
Now, Drew McDonough spends his days amid the industrial-size kettles that gently simmer with 40-gallon batches of buttery toffee sauce.
Having a job, he said, “feels fabulous. Not just for me but for my parents as well. They were sometimes frustrated with what I was going through, with the job hunt.”
After graduating from Loras College in Dubuque, Iowa, with a degree in media studies in 2011, McDonough searched for a job for two years before he learned about Have Dreams.
He and the other men have done so well at the bakery that Kroll agreed to have a class of three more interns start in January.
McDonough will continue to work 20 hours a week and also serve as a mentor. Training the newest workers is something that
McDonough admits “may be a bit of a challenge.”
But that’s OK with Kroll. “I’m glad he’s nervous,” she said. “We want to push them past their comfort zone, because we know when they’re in another employment setting they’re going to be pushed. We want to help them work through those stresses right now, and then be able to step up and do the job.”
Kroll can’t staff her bakery entirely with people with autism. And so, administrators at Have Dreams are searching for other businesses where graduates of the bakery program can work.
“We need to help business owners understand, like Jean does, that there is an economic benefit to employing this population. This is not just a feel-good story,” said McCain, of the Coleman Foundation. “Think of how many manufactures there are in Chicago who have some discreet, repetitive tasks that need to be done and that might be well-suited to the folks at Have Dreams.”
As McDonough’s shift comes to an end on that recent December day, he carefully affixes a toffee-colored label to each of the 67 boxes of cakes that he packaged for shipment. He grabs a broom and sweeps the bits of shortbread and the sprinkling of cocoa powder that had fallen here and there on the bakery floor.
When the clock hands point toward 4 o’clock — the end of his shift — he approaches Kroll. “This area is swept,” he says.
“Very good. Want to say goodbye to the other guys?” she replies. (Kroll is still trying to help him with social skills.)
McDonough walks a fast loop around the bakery with his hand up in a perfunctory wave. “See you,” he says flatly to each person he passes. Then he clocks out at the computer, exchanges his apron for his jacket and strides quickly to the door.
As he rushes past Kroll, he barely looks up.
“Bye,” he says.
“Thank you, Drew!” Kroll calls.
Afterward, Kroll stands in the bakery, an apron around her waist and a pile of orders in her hand. “It was a great day. A really nice, regular day,” she says. McDonough had worked independently, taken ownership of his task and cleaned up afterward. “He has grown so much.”
What’s more, she says, he has carried his weight and helped her business grow. As he develops more skills, she says, he’ll earn wage increases, “just like everyone else.”
“This is a good business decision,” she says. “It just so happens that it’s also a really good social decision and a good moral decision too.”