By Caroline Fredrickson
Opinion
The Philadelphia Inquirer.
If only it were as easy as “leaning in.” Unfortunately, for most American women, cracking the glass ceiling on the way to the executive suite is as relevant to their lives as a fairy tale. Instead, they face challenges much more fundamental, such as earning a living wage, providing for their children, and, if there’s anything left over, trying to save for retirement.
Mathilda Olafsson, my great-grandmother, left Sweden at 18 to escape poverty, sailing steerage to Boston alone. She got a job as a scullery maid, with days full of backbreaking labor and meals made up of scraps from her employers’ plates. She was subject to the petty and sometimes abusive whims of her employers.
As a teenager, I found Mathilda’s story romantic, so far in the past, so different from today. Sadly, it is not.
Shockingly, many domestic workers, and women in other professions dominated by females, have little more legal protection than Mathilda and her peers did more than a hundred years ago.
We tend to think things aren’t so bad today. After all, we have banned discrimination, required equal pay for equal work, and adopted family-leave legislation. But few people know that as we adopted progressive laws to improve the wages and working conditions of many, we left many behind. During the New Deal, President Franklin Roosevelt bargained with the “Dixiecrats,” trading the rights of African-American and women workers in order to secure enough votes for bills providing a minimum wage, overtime and the right to join a union.
Subsequently, legislation barring discrimination in employment has excluded many women. Not just nannies, home-health aides, and housekeepers, but also farmworkers, small-business employees, independent contractors, temporary workers and others who have almost no protection under the law. The numbers add up fast.
But even if all women had protections against discrimination and the right to fair wages, they are also the ones who bear the brunt of our flimsy family-leave policies and our abysmal lack of child care. In 1993, the United States finally adopted the Family and Medical Leave Act, providing some workers with the right to take 12 weeks of leave for the birth or adoption of a child or other family health-care needs. But the act’s benefits are limited to a small number of employees: More than 40 percent of private-sector workers don’t qualify and the workers with least access to leave are those most in need, younger, low-wage women of color.
And since the act provides for only unpaid leave, even those mothers who qualify often don’t use it because they can’t afford to lose wages. With families dependent on their wages, many women return to work shortly after giving birth despite having complications from cesareans, difficult pregnancies, or postpartum depression.
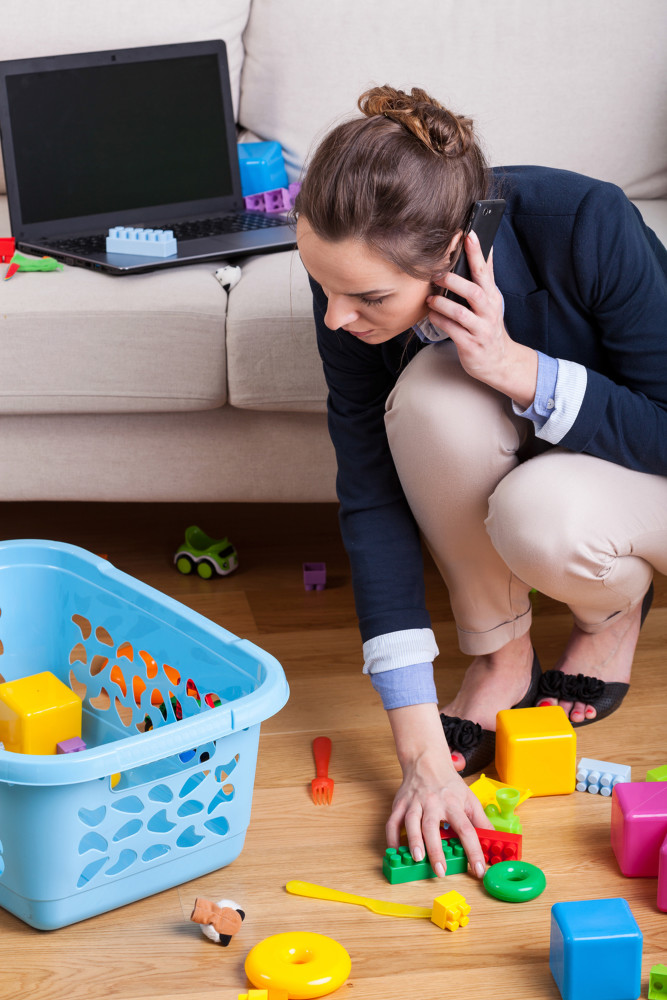
And once a child is born, mothers may face an even bigger challenge: child care. We hear about the upper-middle-class conundrum of whether a mother should stay home because she is paid less than the father, the cost of child care being more than her earnings, and the worry of how “opting out” might affect her income over the long term.
A late night at the office or an unexpected dinner out, while a nanny provides child care, is a part of life for some privileged parents. But few people consider what happens when nannies have children of their own. Middle-class families suffer too, as child care takes a huge bite out of their income, slots fill up and quality is questionable.
We have a ways to go as a nation before the glass ceiling becomes the most significant problem for women. More and more of our jobs lack benefits, fewer of us are part of a union, almost none of us have decent or affordable child care, and many are denied sick days or family leave.
So let’s take up the challenge of making caregiving and work compatible and face the reality that, except for a tiny elite, “leaning in” is as germane to most women’s lives as the king of Sweden was to my great-grandmother Mathilda.
___
ABOUT THE WRITER
Caroline Fredrickson is president of the American Constitution Society and author of “Under the Bus: How Working Women Are Being Run Over.” She wrote this for The Philadelphia Inquirer.